As use of digital payments and online banking mushroom in India, instances of fraud have risen just as fast. India ranks 1st worldwide for identity thefts – 27.2 Million adults were compromised in FY22. Enterprises had to spend 1.3 Billion person-hours to resolve these identity thefts.
Today’s digital-first businesses cannot afford authentication methods that frustrate customers or expose them to fraud. Traditional SMS OTPs, while familiar, have become a weak link in the security chain because of delays, delivery failures, SIM-swap frauds, and phishing exploits. For enterprises handling millions of logins and transactions every month, every failed OTP means a broken customer experience and potential revenue loss. OTP-less authentication has emerged as the necessary evolution in this landscape. It enables faster, more reliable, and secure verification while keeping user journeys friction-free. In India, where mobile-first adoption is driving e-commerce, banking, and fintech growth, enterprises are now making OTP-less solutions their default mode of authentication to combine compliance with customer trust.
Identity-related frauds in UPI alone led to ₹200 Crore of losses to account holders FY21. This is estimated to be ₹500 Crore in 2023 (estimated to be proportional to the growth of transactions). Further, the recovery rate of these losses stands at an abysmal 2-8% of the lost money. In FY23, the Indian banking system recorded 13,530 fraud cases. In May 2023, the Reserve Bank of India reported the highest incidence of fraud in digital payments.
SIM swap or SIM-jacking has been identified as one of the most prevalent frauds in India that exploits the inherent weakness of OTP via SMS. Recently, a news report on TOI quoted RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das urging regulated entities to adopt better alternatives to OTP via SMS for second-factor authentication. Recently, ICICI Bank was quoted in a news report on the Times of India identifying types of identity fraud faced by their consumers.
India’s market for authentication is at an inflection point. With over a billion mobile users and the rise of digital public infrastructure like UPI and Aadhaar-linked services, the volume of daily authentications is staggering. BFSI institutions are leading adoption, driven by RBI’s mandate for strong customer authentication and their own need to reduce fraud losses. E-commerce platforms are close behind, using OTP-less flows for login and cash-on-delivery confirmations. Healthcare and government services are also exploring these solutions to secure sensitive records and citizen-facing platforms. The momentum is clear OTP-less authentication is not a futuristic concept but an urgent enterprise priority across sectors in India.
To address the above, Times Mobile recently announced a partnership with Sekura.id to bring an SMS OTP-less authentication method to India called SAFr Auth. This technology verifies mobile possession via SIM in real-time without the use of a username, password or OTP to deliver a superlative customer experience.
How SAFr Auth Works
OTP-less authentication replaces the dependency on SMS or email codes with modern mechanisms like device binding, push notifications, WhatsApp verified templates, and cryptographic tokens. Instead of waiting for a one-time password that could be delayed or intercepted, the user’s identity is validated directly against secure identifiers such as their registered device, their consented WhatsApp account, or biometric approval. This reduces points of failure and eliminates OTP forwarding or phishing loopholes. Unlike SMS OTP, where delivery depends on operator networks and DLT filtering, OTP-less delivers consistent performance with measurable audit trails, giving enterprises both security and efficiency at scale.
When using the traditional SMS based OTP, the user has to go through a 7 step process shown below to authenticate themselves –
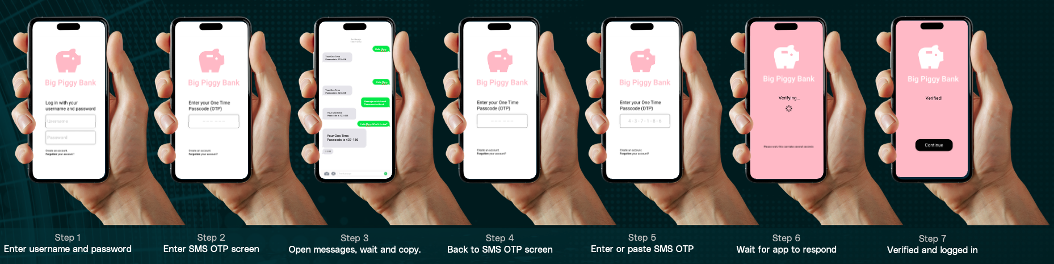
In addition to being prone to customer abandonment, this also leaves the user open to SIM swap and phishing attacks. In contrast, SAFr Auth has a simple 3 step process shown below –
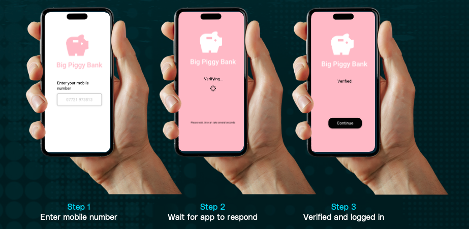
In addition, SAFr Auth also eliminates fraud via the following process –
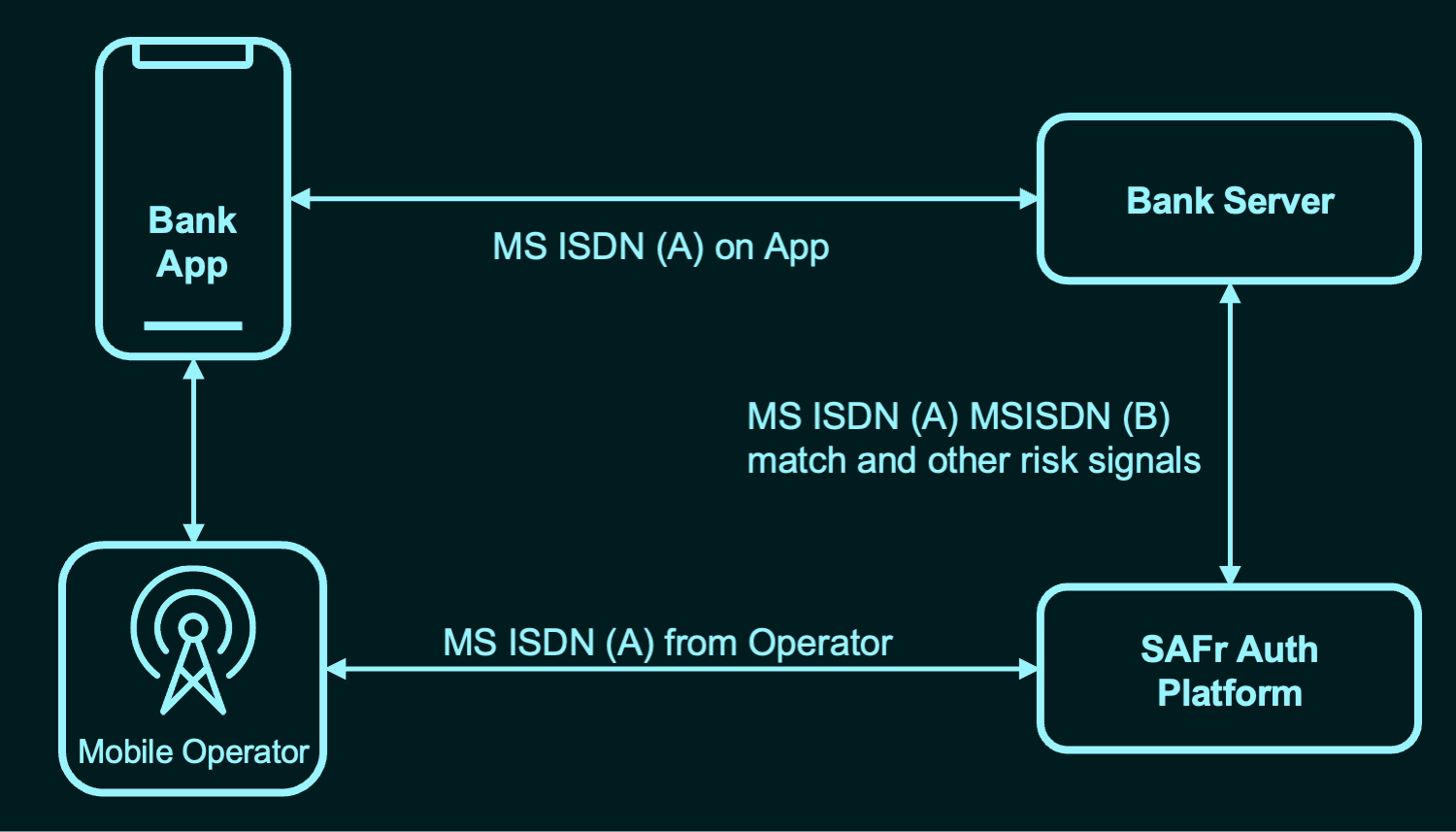
SAFr Auth verifies that the mobile number provided on the app (MSISDN A) matches the one detected by the mobile operator (MSISDN B). It also analyses additional risk signals to thwart phishing attacks.
This server-based architecture based on OAuth 2.X protocol that integrates the enterprise (bank) server and mobile network operators enables SAFr Auth to eliminate 90% of the fraud associated with two-factor authentication methods like OTP SMS.
An effective OTP-less solution is more than a feature. It is an orchestration of APIs, consent flows, and analytics. When a user initiates an authentication request, the orchestration layer checks their identity against stored device credentials or initiates a WhatsApp verified message template for consent. Webhooks capture responses in real time, logging data points such as message delivery, read status, timestamp, and user confirmation. This information flows directly into the enterprise CRM or risk management system, where it is combined with fraud scoring models. The architecture ensures compliance with RBI guidelines while maintaining audit-ready trails that enterprises can present during regulatory checks. Such a structured approach transforms authentication into a seamless part of the customer journey rather than a disruptive checkpoint.
SAFr Auth has been successfully deployed in a number of banks. A leading tier-1 high street bank in UK reported significant reduction in fraud and a smoother customer onboarding process leading to a 35% improvement in account approvals and a 25% reduction in customer abandonment. Yet another tier-1 bank in UK reported significant reduction in SMS OTP passcode related social engineering and account takeovers.
Competitive Landscape & Comparisons
Many companies are now trying to replace the old SMS OTP system because it is slow, inconvenient, and easy for fraudsters to attack. While Times Mobile’s SAFr Auth is one solution.
Enterprises switching from SMS OTP to OTP-less authentication report a double impact: cost efficiency and risk reduction. At scale, SMS OTP costs can easily run into crores of rupees annually, with each authentication costing between ₹0.12 to ₹0.18. For an enterprise processing 1 million authentications a month, even a 20% drop in SMS traffic through OTP-less channels represents significant savings. More importantly, OTP-less prevents high-value fraud like SIM swaps and phishing, which can cause irreparable brand damage and regulatory penalties. The ROI is not just about cutting expenses; it is about preserving trust and ensuring that customers complete their journeys without friction, leading to higher lifetime value.
Traditional SMS OTP
- How it works: A 6-digit code is sent to the user’s phone by SMS.
- Pros: Simple to understand, works everywhere.
- Cons: Risky (codes can be stolen via phishing or SIM swap), slow, users get frustrated typing codes.
SAFr Auth (Times Mobile + Sekura.id)
- How it works: Verifies the mobile number directly with the mobile operator. No OTP required.
- Pros: Very secure, stops SIM swap and phishing fraud, only 3 steps instead of 7, seamless for users.
- Cons: Needs integration with telecom operators, may require fallback in areas with weak network coverage.
The next phase of OTP-less authentication in India will be shaped by AI, regulatory innovation, and platform convergence. Artificial intelligence is already being integrated into fraud detection, using behavioral analytics to identify abnormal login patterns and trigger stronger verification flows. With WhatsApp Payments and ONDC gaining traction, authentication and payments are converging into unified journeys. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP) will further shape how enterprises store and process consent logs, making audit readiness and transparency non-negotiable. As enterprises plan for the future, OTP-less will not just remain a fraud-prevention tool but evolve into a cornerstone of digital trust.
Conclusion
OTP-less authentication is no longer an experiment; it is the foundation for secure, scalable, and customer-friendly digital experiences in India. SMS OTP, while familiar, has reached its limits in reliability and risk management. Enterprises that continue relying on outdated methods risk higher fraud losses, broken customer trust, and mounting compliance pressure. The way forward is clear: OTP-less authentication delivers speed, security, and confidence at enterprise scale. Businesses that embrace it today will be the ones that define digital trust in India’s mobile-first economy tomorrow.




No responses yet